Chapter 1 - Introduction to Cloud Computing and AWS
- Virtualization is what makes cloud computing possible - pooling resources from a server for multiple tenants
- Scalability refers to ramping up of resources, Elasticity refers to reduction of capacity
- Cloud computing converts IT spending from a Capital Expenditure to Operating Expenditure
- AWS divides its servers and storage devices into globally distributed regions and, within regions, into availability zones (an isolated physical datacenter within an AWS region).
- A VPC is a network address space where you can create network subnets and associate them with availability zones.
- AWS Shared Responsibility Model - AWS is responsible for the cloud itself while the clients are responsible for what happens within it
- The convention for naming tags/labels is project1:server1
AWS has 6 core categories:
- Compute
- Networking
- Storage
- Database
- Application Management
- Security & Identity
AWS Support Plans
- Basic - free with every account
- Developer - $29/mo Access to cloud support associate
- Business - $100/mo faster response and support API
- Enterprise - All other feature, direct access to solutions architect, infrastructure guidance and consultation
Services for Working with AWS
- AWS Organizations - Allows for Multi-Account AWS environment
- AWS Control Tower simplifies AWS experiences by orchestrating multiple AWS services on your behalf while maintaining the security and compliance needs of your organization.
- AWS Service Catalog lets you centrally manage your cloud resources to achieve governance at scale of your infrastructure as code (IaC) templates, written in CloudFormation or Terraform.
- AWS License Manager - Manage your software licenses and fine-tune licensing costs
- AWS Artifact is a digital repository that allows customers to download compliance-related information about their AWS accounts and services.
- AWS CLI - for Command Line management
- AWS SDK - for application integration using popular programming languages
Services for Migrating to AWS
- AWS Migration Hub is a service that helps organizations track their progress as they migrate their workloads to the AWS cloud.
- AWS Application Migration Service (replaced AWS Server Migration Service) for moving your on-premises and cloud-based applications
- AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) is a managed migration and replication service that helps move your database and analytics workloads to AWS
- Application Discovery Service inventories your datacenter, collects information about your applications, and then creates a configuration model of your applications and their dependencies.
Chapter 2 - Compute Services
Am AMI will be available in only a single region. There are 4 kinds of AMI’s
- Amazon Quick Start AMIs
- AWS Marketplace AMIs from industry vendors
- Community AMIs from independent vendors
- Private AMIs
Instance Types
| Instance Type Family | Types |
|---|---|
| General Purpose | Mac, T4g, T3, T2, M6g, M6i, M6a, M5, M5a, M5n, M5zn, M4, A1 |
| Compute Optimized | C7g, C6g, C6i, C6a, Hpc6a, C5, C5a, C5n, C4 |
| Memory Optimized | R6g, R6i, R5, R5a, R5b, R5n, R4, X2gd, X2idn, X2iedn, X2iezn, X1e, X1, High Memory, z1d |
| Accelerated Computing | P4, P3, P2, DL1, Trn1, Inf1, G5, G5g, G4dn, G4ad, G3, F1, VT1 |
| Storage Optimized | Im4gn, Is4gen, I4i, I3, I3en, D2, D3, D3en, H1 |
- General Purpose provides a balance of memory, compute and network resources
- Compute optimized for more demanding web servers and high end machine learning workloads
- Memory optimized work well for intensive database, data analysis and caching operations
- Accelerated computing are recommended for high-performance computing (GPU intensive), financial, AI and medical research workloads
- Storage optimized fast read and error with low latency access to EBS volumes
EC2 Storage Volumes
Volumes are your machine’s storage drives. These are the available kinds
- Elastic Block Store (EBS) Volumes - AWS guarantees the reliability of data even if the drive fails. It replicates volumes across multiple availability zones
- EBS-Provisioned IOPS SSD - for applications that require intense I/O operations
- EBS General Propose SSD for most regular server workloads that deliver low latency
- HDD Volumes for large data stores where quick access is not required using spinning hard drive
EC2 Instance Private IP Range
- From 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8)
- From 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12)
- From 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0/16)
EC2 Pricing Models
- On-Demand
- Reserved - pay up front
- Spot - bid for an instance on the Amazon Market. Recommended for workloads that require predictable service
Containers
There are 2 ways to run containers on AWS
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) - uses Amazon EKS Distro, a Kubernetes distribution built and maintained by AWS. Amazon EKS Distro makes it easier to create reliable and secure clusters.
AWS Fargate - used with Amazon ECS or Amazon EKS to easily run and scale your containerized data processing workloads.
Chapter 3 AWS Storage
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
- Also good for backups, log files, disaster recovery images, big Data at rest, Hosting static sites
- Global service though you must pick a region where your data must reside
- An object storage system with a flat storage file placement. The object keys determine how they’re grouped in folders
- Bucket names must be unique - s3.amazonzws.com/bucketname
- S3 Transfer Acceleration can speed up large file uploads
- Server Side encryption can be done with S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3), KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS), or Customer-Provided Keys (SSE-C)
- Logging is disabled, and if enabled logs are stored on another bucket
- Durability scores refer to infrastructure failures, whereas Availability scores are for downtimes
- Standard storage is 99.99% guaranteed available (<9hrs downtime / yr), Standard-IA and Intelligent Tiering are 99.9%, and One Zone-IA is 99.5% available
- Data is eventually-consistent which means S3 has low-latency read/write access to files
- Objects you store within an S3 bucket can be as large as 5 TB, anything above 100 MB should be uploaded with Multipart Upload, and objects above 5 GB must use Multipart Upload.
- Access control list is recommended via IAM and S3 Bucket policies instead of Access Control List (ACL)
- Amazon S3 Glacier storage class provides long-term storage for data needed in infrequent circumstances. Retrieving data is designed to be slow
- Amazon Macie is a data security service that uses machine learning (ML) and pattern matching to discover and help protect your sensitive data stored in S3.
Other Storage-Related Services
- Elastic File System (EFS) - Create and configure shared file systems simply and quickly for AWS compute services—no provisioning, deploying, patching, or maintenance required. Designed for access in a VPC on Linux instances. Stored across multiple zones in a region
- Amazon FSx (File System X) for file-sharing services specific (X) certain servers
- AWS Storage Gateway for integrating local to cloud storage service
- AWS Snow Family for moving terabytes of data using a physical device shipped by Amazon
- AWS DataSync is a data-transfer service that simplifies, automates, and accelerates moving and replicating data between on-premises storage systems and AWS storage services.
Chapter 4 Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
VPC provides the networking layer of EC2.
- It’s logically isolated from all other networks though you can connect it to other networks, VPC’s or the internet
- Exists in only the region it’s created
- It consists of a range of an IPv4 range in a Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) block. The recommended addresses are defined in RFC 1918 to avoid conflicts with public internet addresses, specifically these CIDR notation 10.0.0.8/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16. The maximum prefix is /32
- IPv6 addresses are assigned by AWS
- Secondary CIDR IPv4 blocks should be in the same IP range
- Subnets are logical containers within a VPC that groups your EC2 instances. Every instance must exist under a subnet.
- AWS reserves the first 4 and last IPv4 address in your CIDR block for every subnet - 192.168.0.0, .1 (Implied router), .2 (DNS Server), .3 (Reserved), .255
- Route Tables (prefixed rtb) control traffic ingresses and egresses within your VPC
- Security Groups (prefixed sg) function as a firewall that controls traffic to and from your instances Elastic Network Interface (ENI). Each VPC has a default Security Group you can’t delete but can be modified to suit your needs. It’s stateful - it tracks and replies to traffic
- Network Access Control Lists (prefixed acl) also functions as a firewall similar to Security Groups but it is attached a Subnet. It’s stateless - it does not track nor reply to traffic unless you allow it to.
- AWS Network Firewall is a dedicated service if you need to protect multiple VPCs and Subnets - even across different AWS accounts
- Public IP Address - optional when you launch an instance in a subnet
- Public Elastic IP Address (EIP) - allocated by AWS you can associate to an Elastic Network Interface
Elastic Network Interfaces (ENI) allow an instance to communicate with other network or AWS services. It also allows one to SSH or RDP in your instance.
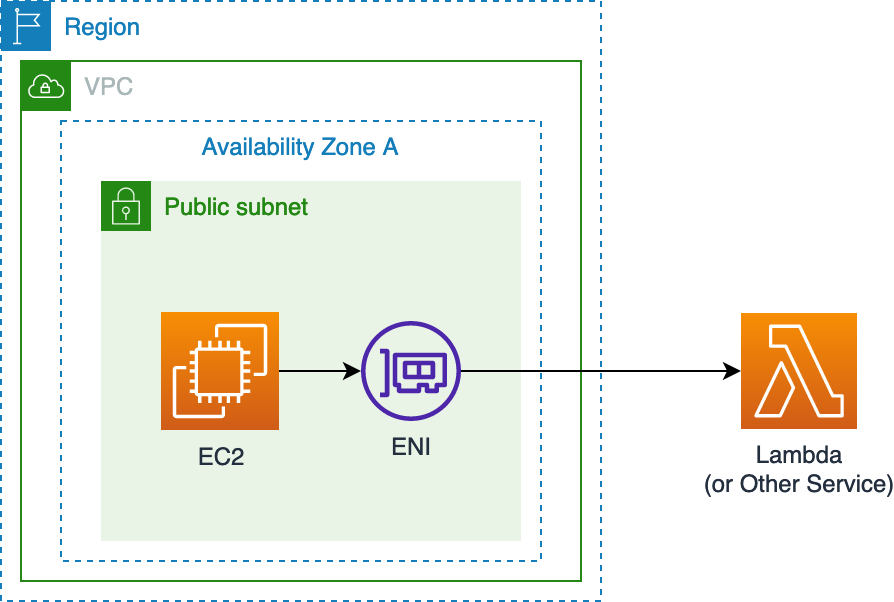
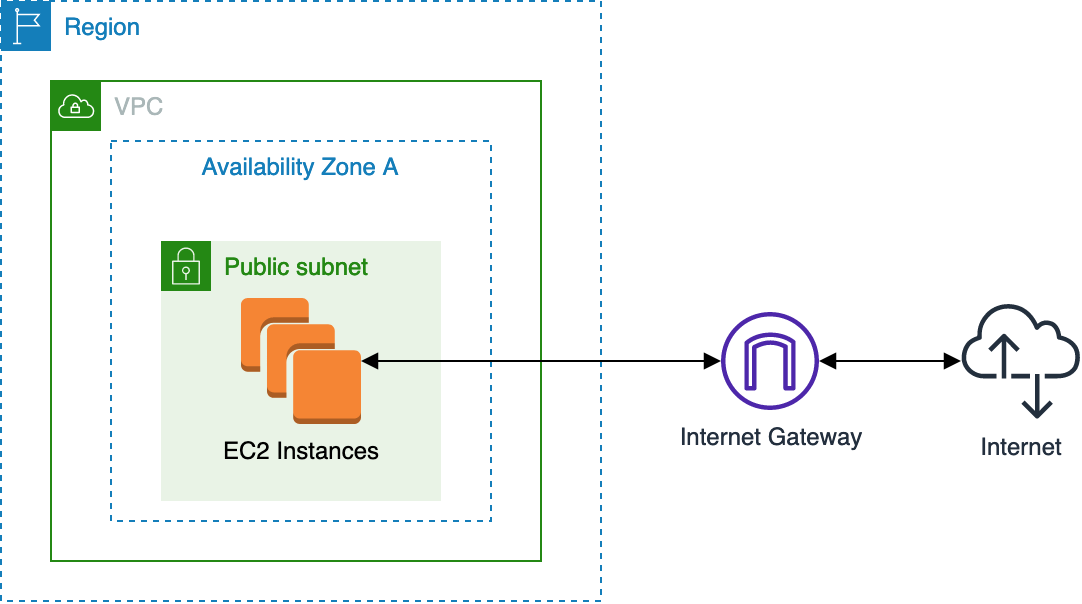
Internet Gateway (prefixed igw) gives instances ability to obtain public IP’s, connect and receive requests from the internet. The default VPC has one, but you have to create it manually for custom VPC’s
NAT Gateway (prefixed ngw) is a managed Network Address Translation (NAT) service. Unlike Internet Gateway, it allows instances with no public IPs to access the internet. It scales automatically and can exist in only 1 availability zone.
A NAT Instance functions (and sets up) the same way as a NAT Gateway. It’s a Linux EC2 instance that does not automatically scale. One advantage of it over NAT Gateway is you can use it as a bastion host to instances that don’t have a public IP.

Other VPC Connectivity Concepts
- AWS Private Link - Establish connectivity between VPCs and AWS services without exposing data to the internet
- VPC Peering - A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
- AWS Site-to-Site Virtual Private Network - By default, instances that you launch into an Amazon VPC can't communicate with your own (remote) network. You can enable access to your remote network from your VPC by creating an AWS Site-to-Site VPN (Site-to-Site VPN) connection, and configuring routing to pass traffic through the connection.
- AWS Transit Gateway - on premise to VPC connectivity. It connects your Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks through a central hub. Most common uses are Centralize/Isolated Router, Peering, or Multicasting
- AWS Direct Connect - on premise to VPC connectivity. It creates a dedicated network connection to AWS - bypassing the internet altogether. You can send data between AWS Direct Connect locations to create private network connections between the offices and data centers in your global network.
Chapter 5 Database Services
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
- Managed service for OLTP (frequent read/write) databases
- An RDS instance exists in a VPC you specify
- You can’t SSH into an RDS directly
- MariaDB is a drop-in binary replacement for MySQL database engine
- Amazon Aurora is a drop-in binary replacement for MySQL and PostgreSQL. It offers an on-demand, autoscaling configuration thru Amazon Aurora Serverless
- For Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle, you can have License Included or Bring Your Own License respectively
- Instance Classes can be Standard (db.m6i 512GB memory, 128 vCPU), Memory Optimized (db.x1e 3,904GB memory, 128 vCPU, 14K Mbps throughput), Burstable Performance (db.t4g 32GB memory, 8 vCPU, 2048 Mbps throughput)
- You can have 5 replicas for RDS, and 15 for Aurora. Replica data are asynchronously written. It may be used as a recovery database but note that its asynchronous nature may lead to loss of data
- RDS can have a multi-availability zone deployment - Primary RDS in 1 AZ and a standby RDS in another AZ for failover. For MySQL and MariaDB, read replicas can be created in a different region
- A read replica accepts queries, whereas a standby instance in a multi-AZ cannot
- RDS EBS volume snapshots are stored in S3
- RDS can automate backups - default 30 min w/in 8hrs, archives every 5mins to S3, retention up to 35 days
- Amazon RDS Proxy maintains a pool of established connections to your RDS database instances. It minimizes application disruption from outages by automatically connecting to a new RDS instance while preserving application connections.
Amazon Redshift
- Managed data warehouse (OLAP complex queries on large datasets) service
- Based on PostgreSQL
Nonrelational (NoSQL) Databases
- Optimized for unstructured, schema-less data
- Non-key queries are naturally slow
- DynamoDB is a managed non-relational database from AWS. It can store an item up to 400KB
Chapter 6 Authentication and Authorization—AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- AWS accounts come with a root user that has full rights over all services
- An IAM Policy contains Effect (Allow/Deny), Action (operations it can perform), and Resource
- In cases where multiple IAM policy Effects to a resource is in conflict - an “Allow” and a “Deny”, AWS resolves it by denying the action
- An entity that can take an action on AWS is called a Principal - which can be a User, Group or Role
- Using the root user for day-to-day activity is not advised. Rather, first and foremost create an admin user with AdministratorAccess policy to create other users, groups and roles
- Access Keys provide authentication for programmatic or CLI-based access
- An IAM Role is an identity within your AWS account that has specific permissions. It has no password or access key. It is similar to an IAM user, but is not associated with a specific person. Use this for Federated User access, Temporary IAM permissions, Cross-account access, and Cross-service access
- Amazon Cognito can add sign up and sign in to your applications (Identity Pools) as well as temporary user (User Pools) access to AWS services.
- AWS IAM Identity Center (Successor to AWS Single Sign-On) enables multi-account access to your AWS accounts, single sign-on to your applications and Windows EC2 instances
- **AWS Key Management Service **(KMS) is a fully managed service for controlling system-wide encryption
- AWS Secrets Manager manages the lifecycle of secrets from storage, rotation, and usage monitoring
- AWS CloudHSM (Hardware Security Module) helps you meet corporate, contractual, and regulatory compliance requirements (FIPS) for data security.
- AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) helps securely share your resources across AWS accounts, within your organization or organizational units (OUs), and with IAM roles and users for supported resource types.
Chapter 7 Cloudtrail, CloudWatch, and AWS Config
CloudTrail for logs of every AWS resource change. It monitors and records account activity across your AWS infrastructure
- Logs both API and non-API actions in S3
- By default logs 90 days of management events but not data events from high-volume data plane services like S3, Lambda, DynamoDb
- If you need more than 90 days, you have to create a “trail” that outputs a JSON file to an S3 bucket of your choice. Max of 5 trails per region
- Non-global service changes are logged specific to their region
CloudWatch for logs of AWS performance metrics. It collects and visualizes real-time logs, metrics, and event data of applications on AWS
- Organizes logs with namespaces, e.g. AWS/S3, AWS/EC2, …
- Basic monitoring metrics are recorded every 5 minutes
- Detailed monitoring metrics (from API Gateway, Cloudfront, EC2, Beanstalk, Kinesis, MSK, S3) are recorded every 1 minute
- You can choose any of these actions for when a Cloudwatch sets an alarm - Send an SNS topic event, Auto Scale by adding/removing instances, perform EC2 operations
- For more detailed event handling, consider using EventBridge which allows you to choose specific AWS services to use based on rules you set per type of event
AWS Config continually assesses, audits, and evaluates the configurations and relationships of your resources on AWS at a point in time.
- It deals with the state of a resource at any point in time
- It uses configuration items to build a history for each resource
- You define rules for evaluating the state of your resources and allows you to remediate issues the rule can find
Chapter 8 The Domain Name System and Network Routing: Amazon Route 53 and Amazon CloudFront
Amazon Route 53 has 4 focus Areas
- Domain Registration - for ensuring domains are globally unique and accessible
- DNS Management - Uses zones (or hosted zones) for defining DNS Domain. A zone file contains the name, TTL, Record Class and Type, e.g.
example.com. 1h IN NS ns-750.awsdns-30.net - Availability Monitoring
- Traffic Management - policies for latency-based routing on AWS resources in multiple regions, failover routing for when health check fails, and geolocation routing
Traffic Flow - web console for visualizing routing policies
Route 53 Resolver - for managing DNS queries between AWS and on-premise resources
Amazon Cloudfront is a global CDN
Cloudfront will ask for the type of content distribution on set up - Web Distribution for pages and graphics, RTMP (Real Time Messaging Protocol) for S3 videos that support the Adobe protocol. It permits the following origins
- S3 bucket
- MediaPackage channel endpoint
- MediaStore container endpoint
- Application Load Balancer
- Lambda Function URL
- Custom origin of an HTTP Server

Chapter 9 Data Ingestion, Transformation, and Analytics
AWS Lake Formation lets you create a data lake from various sources - either AWS or on-premise. It uses AWS Glue (based on Apache Spark) for ETL and query operations.
AWS Transfer Family enables you to transfer files into and out of AWS using FTP, SSH FTP (SFTP), or FTP over SSEL (FTPS)
Amazon Kinesis (meaning Motion) is a collection of service that lets you work with streaming data.
- Kinesis Video Streams - for image recognition, streaming video, and videoconferencing. Time indexed. It can retain video streams from 1-7 days. As a producer, it can allow multiple consumers to pull data.
- Kinesis Data Streams - ingest and stores streaming (or binary) data (logs, stock trades, location info) from producers. Indexed by partition key and sequence number because data is stored in shards. Each shard gives you 1MB write, 2MB read. As a producer, it can allow multiple consumers to pull data. Somewhat similar to SQS only Kinesis Data Streams provide durable storage.
- Kinesis Data Firehose - ingests streaming data and transforms it (using Lambda functions) before sending to a destination. You must specify a destination for the transformed data when using this service.
Chapter 10 Resilient Architectures
Resiliency is the ability of your applications to recover from failure. It is measured by your application’s “Availability”. The more available your application - the more complex and expensive it can be because of redundancies required to keep the application running all the time.
Cloud applications can fall in 2 categories. The application’s availability score is derived by averaging the scores of each resource
- Traditional - applications that use self-managed AWS resources like EC2 Linux instances, MySQL RDS.
- Cloud-native - applications that use fully-managed AWS resources like Lambda, DynamoDB
EC2 Auto Scaling can use any of these items when setting up policies
- Launch Configuration - old way and you need to create a new configuration if you need changes made
- Launch Template - newer and recommended. Launch templates are versioned allowing you to make changes
EC2 Auto Scaling Options
- Manual - you set the desired number of instances
- Dynamic - capacity changes as traffic changes occur
- Simple - if metrics threshold are reached, it adjusts based on CloudWatch Alarm
- Step Scaling - will keep adding instances incrementally based on a lower and upper bound of the CloudWatch Alarm breach threshold
- Target Tracking - you select a metric and a value, and it will create a CloudWatch alarm for you
- Schedule - uses “scheduled actions” for a predictable load pattern
SQS enables loose coupling between application components by acting as a buffer. It uses 2 types of queues
- Standard - can handle up to 120,000 in-flight messages. Messages are delivered out-of-order and possibly duplicated
- FIFO - can handle up to 20,000 in-flight messages. Messages are delivered in order and is delivered only once.
Chapter 11 High-Performing Architectures
Strategies for getting the most value out of your AWS Resources
Core AWS Services Optimization
- Use auto-scaling for EC2 compute resources
- Use serverless services for elastic compute infrastructure
- Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)-Optimized EBS Volumes
- Cross-region S3 Replication
- Set CloudFront origin to an S3 bucket instead of a load balancer on top of EC2 instances
- Add a load-balancer to distribute network traffic - an application load balancer for Layer 7 (HTTP) protocol, or a network load balancer for Layer 4 (TCP) protocol
Infrastructure Automation
- Use CloudFormation to model your infrastructure stack (group of resources) using JSON or YAML templates
- OpsWorks is a configuration management service (similar to CloudFormation but for 3rd party resources) that helps you configure and operate applications in a cloud enterprise by using Puppet or Chef.
Optimizing Data Operations
- Setup caching with ElastiCache - a fully managed, Redis- and Memcached-compatible service
- Create database read replicas in RDS
Chapter 12 Secure Architectures
Applying security controls to storage, compute and networking resources
IAM Permission Policies
- AWS Managed Policy - pre-built and frequently updated by AWS
- Customer-Managed Policy - policies you create as an account owner
- Inline Policy - embedded policies to an IAM account, with a strict 1:1 relationship to the principal
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) - lets you create, manage, and control cryptographic keys across your applications and AWS services.
AWS Security Token Service (STS) - A web service for requesting temporary, limited-privilege credentials for AWS Identity and Access Management users or for users that you authenticate (federated users).
Services for Monitoring System Health and Vulnerabilities
Amazon Athena is a paid interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze CloudWatch data or any data directly in S3 using standard SQL.
Amazon GuardDuty is a paid service for continuously monitoring traffic on your AWS accounts, instances, serverless and container workloads, users, databases, and storage for potential threats.
Amazon Inspector is an agent-based (AWS Systems Manager Agent) service that looks for vulnerabilities on your EC2 instances.
Amazon Detective takes information from VPC flow logs, CloudTrail, and GuardDuty and places this information into a graph database.
AWS Security Hub is a cloud security posture management service that performs security best practice checks, aggregates alerts, and enables automated remediation. It collects security information from various AWS services, including Inspector, GuardDuty, and Macie.
Amazon Fraud Detector is a fully managed fraud detection service that automates the detection of potentially fraudulent activities online. You define the event you want to assess for fraud. Next, you upload your historical event dataset to S3 and select a fraud detection model type.
AWS Audit Manager helps you continuously audit your AWS usage to simplify how you assess risk and compliance with regulations and industry standards. It makes it easier to assess if your policies, procedures, and activities, also known as controls, are operating effectively.
Services for Protecting Your Network
Network Access Control Lists (ACL) and Security Groups - for defining allowed traffic to and from a subnet
AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) - for monitoring HTTP and HTTPS requests to an application load balancer or CloudFront distribution. You can block traffic based on IP patterns or geo location.
AWS Shield is a managed DDoS protection service. Standard defends Layer 3 and 4, Advanced includes protection against Layer 7 attacks
AWS Firewall Manager simplifies your AWS WAF administration and maintenance tasks across multiple accounts and resources. You set up your firewall rules just once and the service automatically applies your rules across your accounts and resources
Chapter 13 Cost-Optimized Architectures
Costs can differ between AWS regions. These are services for tracking Costs
- AWS Budgets - set custom budgets (daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually) to track your costs and usage, and respond quickly to alerts received from email or SNS notifications if you exceed your threshold.
- AWS Trusted Advisor provides recommendations that help you follow AWS best practices - one of which is Cost Optimization. Examples include identifying idle RDS DB instances, underutilized EBS volumes, unassociated Elastic IP addresses, and excessive timeouts in Lambda functions.
- AWS Pricing Calculator - estimates the cost for your architecture solution.
- AWS Cost and Usage Reports tracks your AWS usage and provides estimated charges associated with your account. It can deliver the report to S3 as a CSV file
Optimizing Compute Cost
- Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances - a billing discount applied to the use of On-Demand Instances in your account. You can pay as No Upfront (monthly), Partial Upfront, or All Upfront
- Savings Plans - This pricing model offers lower prices (measured $/hour) on Amazon EC2 instances usage, regardless of instance family, size, OS, tenancy or AWS Region, and also applies to AWS Fargate and AWS Lambda usage.
- EC2 Spot Instances can help reduce your computing costs when you have flexibility in when your applications can run. It lets you take advantage of unused EC2 capacity in the AWS cloud. Spot Instances are available at up to a 90% discount compared to On-Demand prices. You can use Spot Instances for various stateless, fault-tolerant, or flexible applications such as big data.